
Museum of Modern Day Slavery
The Museum of Modern Day Slavery opened in 2014. It is managed by Elijah Rising, a prayer gathering that aims to end sex trafficking through prayer, awareness, intervention, and restoration. The museum is a big part of that mission and is housed in a former brothel that Elijah Rising negotiated the closure of in 2012. It is the only museum in the USA dedicated solely to interpreting and raising awareness for slavery in the present day.
The location of the museum provides visitors with a rare opportunity to see inside a brothel. Throughout, there is text interpretation that provides information about sex trafficking in Houston. This is supported by a small collection of artefacts that have been collected by the museum's staff and volunteers when conducting field research with victims of trafficking in the city. The museum also draws attention to the victories of abolitionists in the past through text panels to inspire visitors to take action to end slavery in the present.

Canadian Museum for Human Rights
Situated in Winnipeg, at the heart of the Canadian Prairies, the Canadian Museum for Human Rights is the first museum in the world solely dedicated to the past, present and future of human rights. The museum aims to create inspiring interactive experiences for its visitors in order to equip them with the tools needed to make a difference in the lives of others. It is the first museum in nearly five decades to be built outside Canada's National Capital Region, with funding from the Canadian government, after being established by legislative amendments to the Museums Act in 2008. The museum's building was purpose-built, designed to reflect the themes of the museum in the external construction, with a Hall of Hope built in luminous alabaster and outside glass wings surrounding the building represent a dove as a symbol of peace.
The Canadian Museum for Human Rights has ten core galleries as well as two spaces for temporary or travelling exhibitions. All of the displays within the museum feature diverse aspects of human rights. These include: a discursive introductory display about what human rights are, a gallery that explores the perspectives of indigenous Canadian people, and an exhibition that focusses on the stories of Canadian individuals or groups that have had their own 'journeys' with human rights challenges. Another exhibition features an overview of Canada's legal stance on human rights. Other galleries explore human rights from a more global perspective, looking at the Holocaust, other instances of genocide around the world and 'Turning Points' that have marked key changes in international human rights policy. The later galleries on the visitor route explore human rights in the present and their potential in the future, challenging visitors to take action and inspire change. All of these galleries feature the use of digital interactives, film and audio presented from lots of different perspectives, often providing the visitor an opportunity to actively participate with the theme of the exhibition. Built without a collection, the museum has filled its galleries with objects on loan from organisations around the world, both in Canada and abroad. They also have objects donated to them from the people and groups the galleries represent. The museum also has a Tower of Hope that visitors can go up, with views over the city, and an indoor garden of reflection.
The Transatlantic Slave Trade is cited as the first instance of genocide in world history in the 'Breaking the Silence' gallery which explores the role of secrecy and denial in the persecution of genocide and what happened when people spoke out or offered resistance. The centre-piece of the gallery is an interactive table that shows instances of genocide, both through time and across the world, alongside related documents and images. The 'Canadian Journeys' gallery incorporates the narrative of enslaved Africans using the Underground Railroad to escape to freedom in Canada. There are also narratives of more contemporary forms of slavery and human trafficking. Narratives of enslavement have also featured in public programmes at the museum.

Sticks and Stones Project
The Sticks and Stones Project was led by Northamptonshire Record Office and Northamptonshire Black History Association. A group of students from Kingsthorpe Community College investigated slavery past and present, through historical workshops and a trip to the Houses of Parliament. The focus was on the history of slavery but also learning about forms of modern slavery such as sweatshop labour and trafficking. The students produced a short film and an exhibition to highlight the issues important to young people.

Ireland and the Slave Trade
The Ulster's People's College and the South Belfast Roundtable on Racism launched an exhibition to mark the bicentenary at a Northern Ireland Committee for Refugees and Asylum Seekers (NICRAS) conference on slavery at the Linen Hall Library in 2007. A study group of community workers from NICRAS, the Chinese Welfare Association, Black Youth Network, Donegall Pass Community Forum and the Donegall Pass Community Centre produced the exhibition which told the story of Ireland's involvement in the slave trade and its abolition. Attention was drawn to the fact that merchants in Belfast and across Ireland profited by supplying slave plantations with provisions such as beef or salted fish; some owned slave plantations. The exhibition also stressed that a growing number of campaigners often fought both for Catholic Emancipation and the Abolition of Slavery, linking the two experiences of disadvantage. The exhibition also raised the issues of contemporary slavery and racism. The exhibition toured community centres in Northern Ireland.
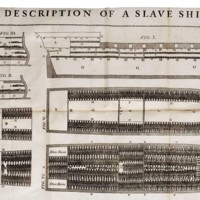
The Print that Turned the World?
The Print that Turned the World? was an exhibition at the London Print Studio, which examined the role played by printmaking in changing public attitudes towards the slave trade and influencing the abolition campaign. The exhibition looked in particular at the influence of the widely publicised print of the slave ship 'Brookes', first published in 1788; the crowded and inhumane conditions depicted had a significant impact on public opinion. The exhibition also examined the role of William Wilberforce in the abolitionist campaign, and the continuation of anti-slavery efforts in modern times. London Print Studio worked with local schoolchildren in creating the exhibition and associated artworks.

Slavery and Anti-Slavery in the Modern World
The City of York lectures in 2007 examined the question: Did the abolition of the slave trade in 1807 really mark the beginning of the end of slavery in the modern world? The University of York organised the public lecture series, which discussed the meaning and legacy of 1807 and the persistence of human bondage and forced labour in the modern world. Speakers included the Right Reverend Dr Alastair Redfern (Bishop of Derby), Aidan McQuade (Director, Anti-Slavery International), Clare Short MP and Trevor Phillips (Commission for Equality and Human Rights).

Marking the 200th anniversary of the Abolition of the Slave Trade
A programme of events to mark the bicentenary was organised by Edinburgh Inter-Faith Association. This included a slavery walk in the footsteps of Robert Wedderburn, a commemoration and thanksgiving service at St John's Church in Edinburgh, and a debate and discussion on the theme 'Trading People - Then and Now'.

Did Slavery End in 1807?
An evening of presentations and music organised by Fife Workers' Educational Association, examining Fife and Scotland's role in the slave trade and abolition, and efforts to end contemporary slavery.

200 Years On: The legacies of enslavement and abolition
The World Development Movement seeks to increase awareness of political views in regards to world economic and social development. The organisation published a briefing in 2007 to mark the bicentenary, exploring the stories of grassroots pressure and the historic and modern campaigns for global justice. In collaboration with the University of Leeds, the World Development Movement also organised two public events looking to explore the lessons to be learned from the struggle to end the slave trade and examining contemporary campaigns in Africa and beyond for global social justice. Speakers included the Kenyan writer and academic Ngugi wa Thiong'o.

Bicentenary of the Abolition of the Slave Trade Act 1807-2007
The official publication from the British Government in response to the bicentenary included a message from Prime Minister Tony Blair. It set out the history of transatlantic slavery and resistance to it, and featured a calendar of upcoming events for 2007 relating to slavery and abolition. The publication also detailed contemporary efforts to end modern slavery. Later in 2007, 'The way forward: bicentenary of the abolition of the Slave Trade Act 1807-2007' reflected on some of the commemorative activity that had taken place in Bristol, Hull, Liverpool, London and Greater Manchester. With a foreword by the new Prime Minister, Gordon Brown, the theme of the publication was 'Reflecting on the past, looking to the future' and it linked efforts for the abolition of historical and contemporary slavery. The publication also looked to how to tackle inequality and poverty in the UK, Africa and the Caribbean.

Breaking the Chains: Eliminating slavery, ending poverty
The official publication to mark the bicentenary from the Department for International Development, with a particular focus on the links between poverty and forms of modern slavery around the world.

Opening of the Wilberforce Institute for the study of Slavery and Emancipation (WISE)
The Wilberforce Institute for the study of Slavery and Emancipation (WISE) was officially opened in Hull in 2006 in anticipation of the city's bicentenary commemorations. The University of Hull research centre specialises in researching the history of slavery, while also examining contemporary slavery and human rights abuses in the present day. The patron of the institute is Archbishop Desmond Tutu and the institute was opened by then President of Ghana, John Agyekum Kufuor. The WISE Humanitarian Wall commemorates historical and contemporary figures in the struggle against slavery, including Olaudah Equiano, Harriet Beecher Stowe and Nelson Mandela.

Parwich 2007 Slavery Season
To commemorate the bicentenary of the Abolition Act, Parwich Church and the Local History Society organised a short series of events. A talk by Alasdair Duncan, 'Operation Reflex', looked at how small rural communities can help combat modern slavery. A talk by Peter Trewhitt explored local involvement links to slavery from pre-historic times through the high reliance on slave work forces in Roman and Saxon times to the influx of wealth from the exploitation of African slaves on Caribbean plantations.

Living Memory Lab
The Living Memory Lab was a two-year project in which people from local communities of Plymouth made three-minute films on the subjects of slavery and abolition and local connections to the slave trade. A series of short training courses in basic film-making were offered as part of the project. The project was a partnership between Plymouth and District Racial Equality Council, BBC South West, the community arts agency Creative Partnerships, in collaboration with Plymouth City Museum and Art Gallery. The DVD was made freely available for use as a teaching aid and community resource.

Drivers for Change: Young People Leading the Way
Drivers for Change was a project led by LifeLine Network, a network of partnerships between community organisations and NGOs with a common aim to fight poverty. In Summer 2007, a team of young people visited Zimbabwe, Sierra Leone and Dominica to explore the ways in which people were combating modern slavery. The trip was inspired by two significant points in history: the 1807 Abolition Act, and the half way point of the Millennium Development Goals, for which 189 nations signed up to a new global partnership to reduce extreme poverty. While in Africa, the group looked at how global partnerships between individuals bring communities together, and assist in countering the impact of poverty and HIV/AIDS. A film was produced documenting the trip, launched at an event was held at the Palace of Westminster.

Testament to a Trade
Testament to a Trade was a play produced to mark the bicentenary, with close reference to Oxfordshire. Written by three local writers, the play was produced by Oxford Theatre Guild in collaboration with Oxfordshire Record Office and the Oxford Playhouse. Testament to a Trade weaves accounts of past and present slavery, and is situated in historical and contemporary contexts, notably 18th century Africa and Oxford, and contemporary Eastern Europe and Oxford. A number of archive materials relating to slavery and abolition are held by Oxfordshire Record Office, information on which inspired elements of the story. A teachers pack was produced to inform similar projects. The play opened at Burton Taylor Theatre in Oxford, and toured venues across Oxfordshire.

Abolition
Abolition was an art project devised and led by artist Jack Brown, in collaboration with Tidemill Primary School in Deptford. It took place during Black History Month 2007, and aimed to commemorate the abolition of the transatlantic slave trade while recognising the existence of modern day slavery. Every child in the school made a 'step', an artwork representing their perspective on the writing, discussion and petitioning that drove abolition. The children visited the Laban Building at Trinity Laban Conservatoire of Music and Dance and laid their step on the studio theatre floor. Taken together, the steps were conceived as a 'stairway to change'.

BOUND
Curated by Predrag Pajdic, BOUND was an exhibition of works by international contemporary artists representing personal perspectives on the physical and psychological impact of slavery on humanity, in historical and modern contexts. BOUND incorporated archival material, conceptual work, photography, video, live art performance, interventions and installations. It was a partnership project between the Open Eye Gallery, FACT (Foundation for Art and Creative Technology) and Tate Liverpool. The exhibition opened at Open Eye Gallery and then ran at various venues across Liverpool. Associated events included open table discussions, talks and film screenings.

La Bouche du Roi
La Bouche du Roi was created by artist Romauld Hazoumé, who lives and work in the Republic of Benin, West Africa. The multi-media artwork is named after a place on the coast of Benin from where enslaved Africans were transported. It comprised 304 plastic petrol can 'masks', each representing a person, arranged in the shape of the woodcut of the Liverpool slave ship Brookes. The aroma of tobacco and spices are represented alongside the terrible smells of a slave ship. The artwork was accompanied by a film showing the motorcyclists who transport petrol illegally between Nigeria and the Republic of Benin. The cans and motorcyclists are metaphors for modern forms of enslavement and resistance. First exhibited at the British Museum in London, La Bouche du Roi toured to the following venues during 2007-9: Ferens Art Gallery in Hull, International Slavery Museum in Liverpool, Bristol's City Museum and Art Gallery, Laing Art Gallery in Newcastle, and the Horniman Museum in London.

Slave Britain: The 21st Century Trade in Human Lives
This photographic exhibition focused on human trafficking was produced by a partnership of Panos Pictures, Anti-Slavery International, Amnesty International, Eaves and UNICEF. Photographer Karen Robinson’s portraits and tales of women trafficked into prostitution explore the devastating impact on their lives. Also on display were David Rose's panoramic photographs of the ordinary British streets where the stories of modern-day slavery have been played out. The photographs were mounted on a cage-like structure which was specially designed for the exhibition at St Paul's Cathedral. The exhibition was also shown in Edinburgh, Hull and Warsaw, and in 2008, in York.